What is BI?
The BI term refers to Business Intelligence . It is a data-driven decision support system (DSS), which helps you to analyze the data and provide actionable information. It helps the business manager, corporate executives, and other users in making their decisions easily.
Business intelligence refers to the applications, technologies, and practices for the collection, analysis, integration, and presents the business information. The purpose of business intelligence is to support better decision making.
Sometimes the business intelligence is used interchangeably with briefing books, reports, query tools, and executive information systems.
The below image shows the benefits of business intelligence, such as:
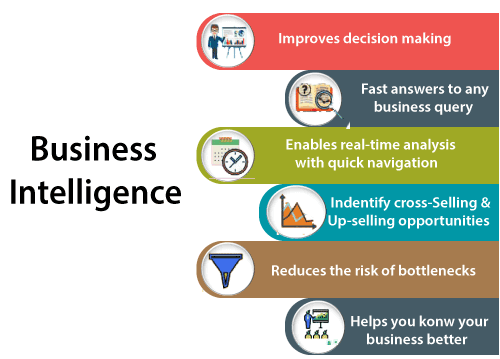
Importance of BI
Business intelligence is used to improve all parts of a company by improving access to the firm’s data and then using that data to increase profitability. Companies that practices BI can translate their collected data into insights their business processors.
Then the insights can be used to create strategic business decisions that improve productivity and accelerate the growth.
Some more potential benefits of business intelligence tools include:
- Driving new revenues.
- It increases operational efficiency.
- It optimizes internal business processes.
- It improves decision making.
- It is gaining a competitive advantage over business rivals.
- It is used in spotting business problems that need to be addressed.
- It can be used in assisting companies in the identification of market trends.
Types of BI Tools
BI combines a broad set of data analysis applications that includes:
- Mobile BI
- Real-time BI
- Operational BI
- Open-source BI (OSBI)
- Collaborative BI
- Location intelligence (LI)
- Software-as-a-service BI (SaaS BI)
- Online analytical processing (OLAP)
- Ad hoc analytics
A business intelligence developer is an engineer who creates, delivers, and maintains business intelligence interfaces. A few examples are query tools, data visualization, and interactive dashboards, ad hoc reporting, and data modeling tools.
Importance of BI
-
Gain New Customer Insights : Business Intelligence allows companies to better monitor and evaluate current client purchasing trends, which is one of the key reasons they invest time, money, and effort in it. Once you’ve figured out what your consumers are buying and why they’re buying it, you can use that data to create products and enhancements that meet their needs and expectations, enhancing your company’s bottom line.
-
Improved Visibility : Business Intelligent organizations have better control over their operations and standard operating procedures since a BI system improves visibility of these functions. The days of sifting through hundreds of pages of annual reports to assess performance are long gone. Business intelligence exposes all parts of your organization, allowing you to immediately identify areas for development and be proactive rather than reactive.
-
Actionable Information : A solid Business Intelligence system can assist you in identifying significant organizational patterns and trends. A business intelligence system can also help you understand the consequences of various organizational processes and changes, helping you to make well-informed decisions and take necessary action.
-
Efficiency Improvements : BI solutions help organizations increase their efficiency, which boosts productivity and, in turn, income. With the use of business intelligence solutions, businesses can effortlessly share critical information across departments, saving time on reporting, data extraction, and data analysis. By making information sharing faster and more efficient, organizations can remove redundant roles and activities, allowing employees to focus on their work rather than data processing.
-
Sales Insight : Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software is used by the majority of sales and marketing teams to keep track of their customers. CRMs are designed to keep track of all customer interactions. Because they store all client contacts and interactions, they have a lot of data and information that can be examined and applied to strategic objectives. Businesses can use BI systems to find new customers, track and sustain existing customers, and provide after-sale services, among other things.
-
Real-Time Data : When executives and decision-makers must wait for reports from multiple departments, the information is prone to human error and may become obsolete before it is even evaluated. Customers may access data in real time via spreadsheets, graphic dashboards, and scheduled emails, among other means, thanks to BI systems. Large volumes of data can be digested, processed, and delivered quickly and accurately when Business Intelligence tools are used.
-
Competitive Advantage : In addition to all of these benefits, Business Intelligence may help your firm obtain insight into what its competitors are up to, allowing it to make informed decisions and plan for future projects.
What are the responsibilities of a BI developer?
Because engineers with similar technology stacks and domain knowledge can be interchanged, the project scope determines the level of involvement for each function. Developing business intelligence interfaces necessitates extensive knowledge of software engineering, databases, and data analysis. As a result, data engineers with a software development background and familiarity with BI can lead the interface development process in part.
Business intelligence software, on the other hand, may offer a number of industry-specific features. BI developers are also aware of the following business domain quirks: This enables them to comprehend business needs, develop appropriate data models, and deploy data representation solutions. As a result, a BI developer’s responsibilities include:
- Setting business requirements for BI tools
- Translating business requirements into technical requirements
- Overseeing the development, deployment, and maintenance of business intelligence software
- Report curation and data modeling
- Participation in data warehouse design, data warehouse documentation, and meta-data storage
- Creating technical documentation for BI tools

