BUSINESS CYCLE
The business cycle is the natural rise and fall of economic growth that occurs over time. The cycle is a useful tool for analyzing the economy. It can also help you make better financial decisions.
The business cycle can also be defined as the downward and upward fluctuations of gross domestic product (GDP) along with its natural growth rate over a long period of time.
The duration of a business cycle is the period of time containing a single boom and contraction in sequence. The time it takes to complete this sequence is referred to as the length of the business cycle.
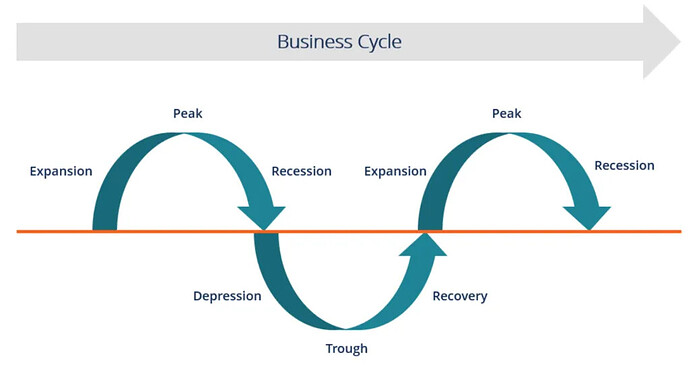
Each business cycle has four phases: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough. They don’t occur at regular intervals, but they do have recognizable indicators.
- EXPANSION: An expansion is between the trough and the peak. That’s when the economy is growing.
- PEAK: The peak is the second phase. It is the month when the expansion transitions into the contraction phase.
- CONTRACTION: The third phase is a contraction. It starts at the peak and ends at the trough. Economic growth weakens. GDP growth falls below 2%. When it turns negative, that is what economists call a recession.
- TROUGH: It is the worst phase in the economy, The trough is the fourth phase. That’s the month when the economy transitions from the contraction phase to the expansion phase. It’s when the economy hits bottom.