Stack Data Structure
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of Last In First Out (LIFO). This means the last element inserted inside the stack is removed first.
You can think of the stack data structure as the pile of plates on top of another.

Stack representation similar to a pile of plate
Here, you can:
- Put a new plate on top
- Remove the top plate
And, if you want the plate at the bottom, you must first remove all the plates on top. This is exactly how the stack data structure works.
LIFO Principle of Stack
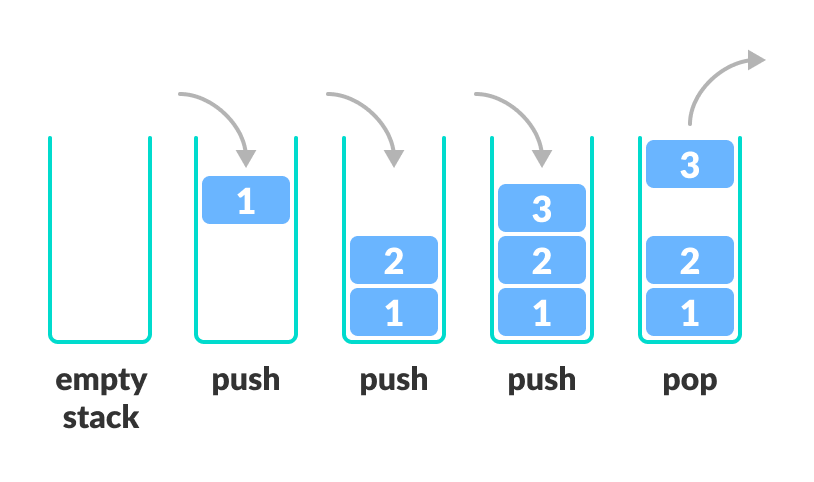
In programming terms, putting an item on top of the stack is called push and removing an item is called pop.
Stack Push and Pop Operations
In the above image, although item 3 was kept last, it was removed first. This is exactly how the LIFO (Last In First Out) Principle works.
Basic Operations of Stack
There are some basic operations that allow us to perform different actions on a stack.
- Push: Add an element to the top of a stack
- Pop: Remove an element from the top of a stack
- IsEmpty: Check if the stack is empty
- IsFull: Check if the stack is full
- Peek: Get the value of the top element without removing it
Stack Time Complexity
For the array-based implementation of a stack, the push and pop operations take constant time, i.e. O(1).
Applications of Stack Data Structure
Although stack is a simple data structure to implement, it is very powerful. The most common uses of a stack are:
- To reverse a word - Put all the letters in a stack and pop them out. Because of the LIFO order of stack, you will get the letters in reverse order.
-
In compilers - Compilers use the stack to calculate the value of expressions like
2 + 4 / 5 * (7 - 9)by converting the expression to prefix or postfix form. - In browsers - The back button in a browser saves all the URLs you have visited previously in a stack. Each time you visit a new page, it is added on top of the stack. When you press the back button, the current URL is removed from the stack, and the previous URL is accessed.