Tableau Data Joining
Data joining is a common requirement in any data analysis. You may need to join data from different tables in a single source or join data from multiple sources.
Tableau provides the feature to join the tables by using the data pane that is available in the Data menu.
A join means combining columns from one or more tables in a relational database. It also creates a set that can be saved as a table, or it can be used as it is.
Joins are specifies into five types:
- Cross Join.
- Inner Join.
- Natural Join.
- Outer Join.
- Left Outer Join.
- Right Outer Join.
- Full Outer Join.
- Self-Join.
Overview of Types of Joins
A join section is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
1. Cross Join: Cross join produces rows which combine each row from the first table with each row from the second table.

2. Inner Join: An inner join returns the matching rows from the tables that are being joined.
ADVERTISEMENT

3. Natural Join: Natural join is not used any comparison operator. It does not concatenate the way.
Only we can perform a Natural Join if there is at least one common attribute that exists between two relations. Also, the attributes must have the same name and domain .
Natural join works on those matching attributes where the values of attributes in both the relation are same.
4. Outer Join: An outer join is an extended form of the inner join.
It returns both matching and non-matching rows for the tables that are being joined.
Types of outer joins are as follows:
i) Left Outer Join: The left outer join returns matching rows from the tables being joined, and also non-matching rows from the left table in the result and places NULL values in the attributes that come from the right table.

ii. Right Outer Join: The right outer join operation returns matching rows from the tables being joined, and also non-matching rows from the right table in the result and places NULL values in the attributes that come from the left table.

iii. Full Outer Join: The full outer join is used to combine tables. As a result, it contains all values from both tables.
When a value from a table doesn’t have a match with the other table, then it returns a NULL value in the data grid.

5. Self-Join: The self-join is used to join a table with itself. It means that each row of the table is combined with itself as well as with every other row of the table.
Creating a Join in Tableau
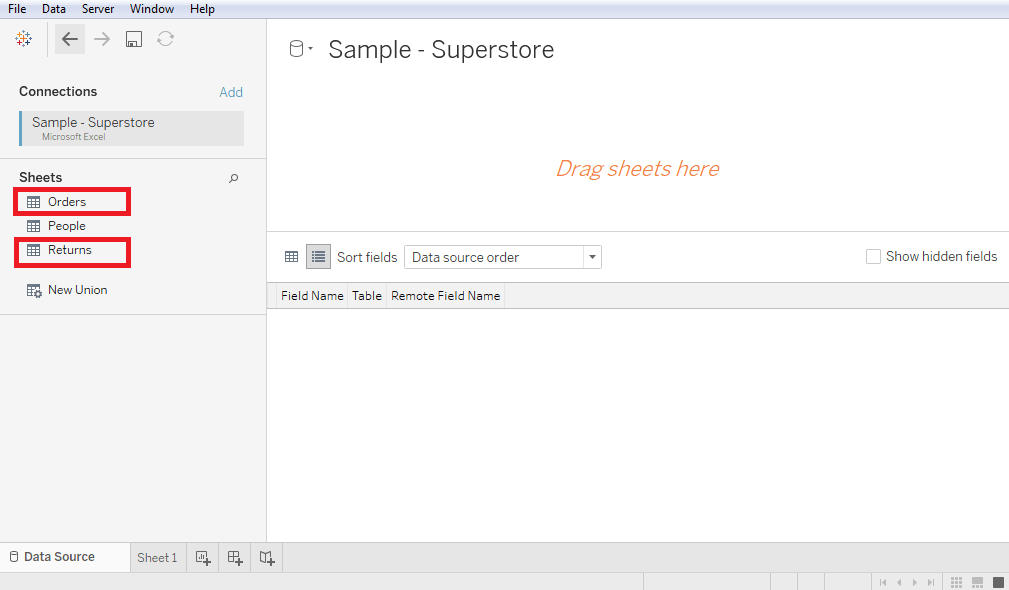
Let’s assume a data source Sample-superstore to create a join between two tables such as Orders and Returns .
- Go to the Data menu and choose Microsoft Excel option below connect .
- Then select sample-superstore as a data source and click the Open button.
- Drag Orders and Returns tables from sheets of the data source to the data pane . After that Tableau will automatically create a join between Orders and Returns tables which can be changed later as per required joins.
- Below screenshot shows the building inner join between Orders and Returns tables by using the Order id field.
Edit a Join Type in Tableau
Tableau automatically creates a type of join between two tables, but it can be changed as per need.
ADVERTISEMENT
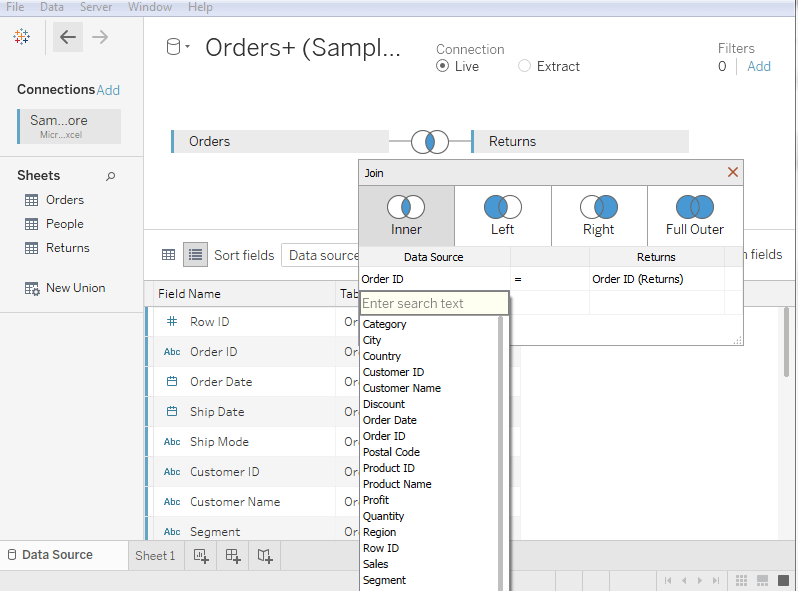
- Click on the middle of two circles that showing the auto-created join.
- After clicking, a popup window appears which shows all the four types of the joins.
- In below screenshot, you can see all the joins such as inner join , left outer join , right outer join , and full outer join .
How to Edit Join Fields in Tableau
- Also, you can change the fields by clicking the Data Sources option to add a new join clause that is available in the join popup window.
- While selecting the field, you can search for the field using a search text box.