A divide and conquer algorithm is a strategy of solving a large problem by
breaking the problem into smaller sub-problems
solving the sub-problems, and
combining them to get the desired output.
How Divide and Conquer Algorithms Work?
Here are the steps involved:
-
Divide: Divide the given problem into sub-problems using recursion.
-
Conquer: Solve the smaller sub-problems recursively. If the subproblem is small enough, then solve it directly.
-
Combine: Combine the solutions of the sub-problems that are part of the recursive process to solve the actual problem.
-
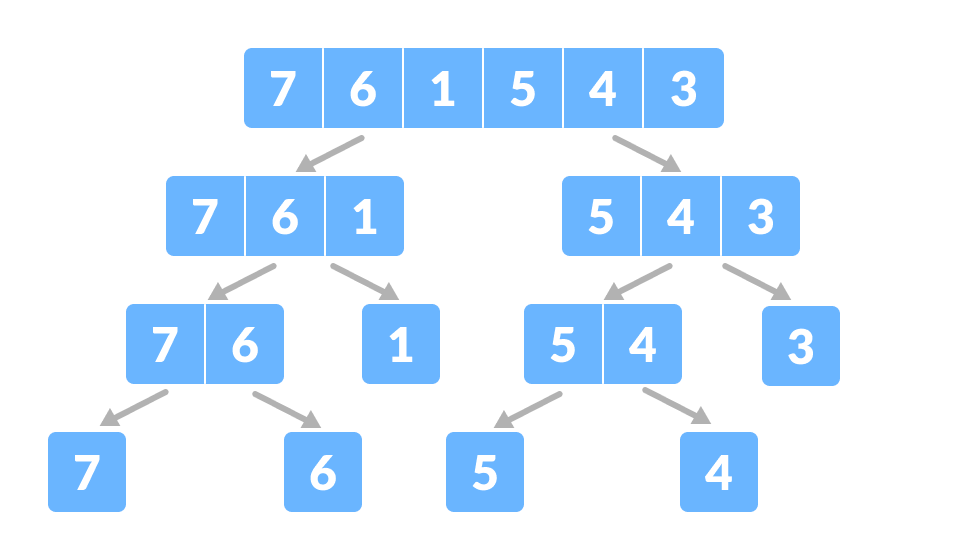
Let the given array be:

Array for merge sort
- Divide the array into two halves.
Divide the array into two subparts
Again, divide each subpart recursively into two halves until you get individual elements.
Divide the array into smaller subparts
- Now, combine the individual elements in a sorted manner. Here, conquer and combine steps go side by side.
Combine the subparts
Divide and Conquer Vs Dynamic approach
The divide and conquer approach divides a problem into smaller subproblems; these subproblems are further solved recursively. The result of each subproblem is not stored for future reference, whereas, in a dynamic approach, the result of each subproblem is stored for future reference.
Use the divide and conquer approach when the same subproblem is not solved multiple times. Use the dynamic approach when the result of a subproblem is to be used multiple times in the future.
Advantages of Divide and Conquer Algorithm
The complexity for the multiplication of two matrices using the naive method is O(n3), whereas using the divide and conquer approach (i.e. Strassen's matrix multiplication) is O(n2.8074). This approach also simplifies other problems, such as the Tower of Hanoi.
This approach is suitable for multiprocessing systems.
It makes efficient use of memory caches.